Types of Spondyloarthritis
Reviewed by: HU Medical Review Board | Last reviewed: October 2022 | Last updated: November 2025
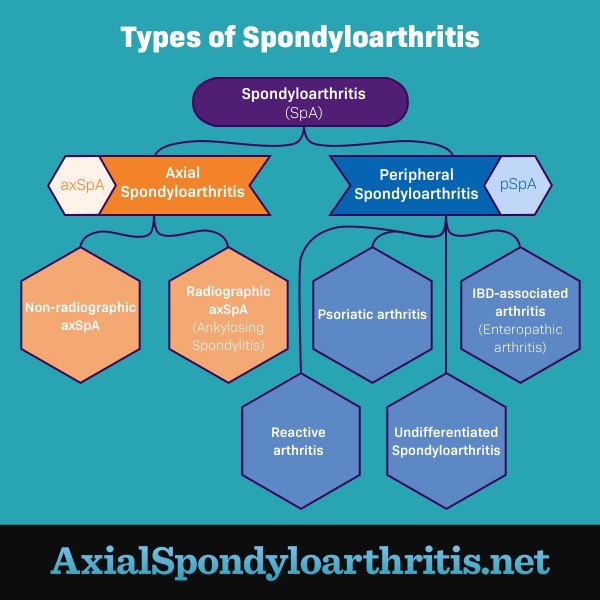
Spondyloarthritis is a type of arthritis that affects the joints and the areas where ligaments or tendons attach to bone (entheses). There are 2 main types of spondyloarthritis: axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) and peripheral spondyloarthritis (pSpA).1
AxSpA mostly affects the spine, though it can also affect other joints in the body. PSpA causes pain and inflammation in joints other than the spine. Several conditions fall within these 2 types of spondyloarthritis. Understanding the type and condition you have can help you manage your symptoms.1
Figure 1. The different types of spondyloarthritis
Axial spondyloarthritis
There are 2 types of axSpA:1,2
- Radiographic (r-axSpA) – Inflammation and bone damage are visible on an X-ray. This condition is typically called ankylosing spondylitis (pronounced “ankle-oh-sing spohn-dih-lie-tiss”) or AS. AS causes long-term inflammation in the joints, which may lead to joint damage and eventually destroy the joints. "Ankylosing" means that joints have become stiff and difficult to move. This happens when the joints grow together, or fuse. “Spondylitis” means inflammation of the spine.
- Non-radiographic axSpA (nr-axSpA) – Inflammation and bone damage are not seen on an X-ray. People with nr-axSpA may have symptoms even though the cause of these symptoms does not show up on X-ray.
People with AS and nr-axSpA often have similar symptoms. AS and nr-axSpA are both forms of axial spondyloarthritis, but they fall on different parts of the disease spectrum. Some people progress to developing AS, but many do not.1,2
Peripheral spondyloarthritis
When symptoms occur mostly in places other than the spine, the condition is called peripheral spondyloarthritis. There are several types of pSpA, including:1,3
- Psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
- Reactive arthritis
- Arthritis with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Undifferentiated spondyloarthritis
Psoriatic arthritis
PsA causes pain, swelling, and inflammation in the joints and tendons. The most common areas of the body that PsA affects are:1,4
- Hands
- Feet
- Wrists
- Knees
- Ankles
Most people with PsA also have psoriasis. This skin rash causes red, scaly patches. In most cases, psoriasis begins before arthritis.4
Some people with PsA have one or more toes or fingers that swell between and around the joints. This is called dactylitis, or "sausage digits.” Some people also have pain and stiffness in the spine.4
Reactive arthritis
Reactive arthritis is a type of arthritis that can result from an infection. The most common cause is a bacterial infection in the urinary tract, gut, or genitals. This type of arthritis is not common. Most people will have signs and symptoms that come and go, then stop within 12 months.5
Arthritis with inflammatory bowel disease
One type of arthritis that can occur in people with IBD is enteropathic arthritis (EnA). About 1 in 5 people with IBD have this complication.6,7
Doctors are not sure why EnA happens. They suspect it is caused by a person's immune system mistaking healthy cells for harmful ones. EnA mostly affects the joints in the arms and legs, but it can occur anywhere in the body.6,7
Undifferentiated spondyloarthritis
A person may be diagnosed with undifferentiated spondyloarthritis when they have spondylitis but do not meet the criteria for a diagnosis of AS or a related disease. Doctors also may use the term "unclassified spondyloarthritis."8
Juvenile spondyloarthritis
Juvenile spondyloarthritis refers to arthritis conditions that begin before the age of 16. JSpA can be either peripheral or axial. The severity of JSpA varies from child to child. Treatment for children is often similar to treatment for adults.9